
KAPPI works as a network of several different independent blockchains, which are called spaces. Each of these spaces is powered through a KAPPI DWARF, ensuring that there are a consistent, high-performing and secure PBFT similar consensus engine wherein the accountability is guaranteed through forks. The KAPPI algorithm is scalable and can be used for proof of stake, public blockchains.The KAPPI is a cryptocurrency that operates a multi-asset proof of stake and has a simple governance system that allows for upgrades and is generally adaptable. The KAPPI DWARF can connect to other spaces allowing it to be extended.
KAPPI is comprised of a network of many blockchains that being powered by KAPPI. KAPPI allows many blockchains to be running concurrently with each other whilst retaining interoperability. At its DWARF, KAPPI DWARF manages multiple independent blockchain ‘zones’, that are also referred to by some as shards. With a constant stream of block commits coming from zones on the DWARF, it can keep up with each zone’s information and its current state. In turn, the zones keep up with the DWARF, but not each other except through the DWARF. Information packets are sent from one zone to another through the DWARF through Merkle-proof posting showing that the information was both sent and received accurately.
Due to the inter-blockchain communication, any zone can be a DWARF for the purpose of forming an acrylic graph, if desired. The KAPPI DWARF blockchain consists of a multiple asset distribution ledger with tokens being individually used or used within a zone itself. Tokens can be moved between zones through a DWARF responsible for preserving any global invariance of the total token value across each zone. Sender, receiver, or DWARF blockchains can commit IBC coin packet transactions. The KAPPI DWARF is the central ledger for the entire system and its security is of primary importance. Each zone can have a KAPPI blockchain that is secured by no less than 4 (or less if not using the BFT consensus) and is secured by a set of validators that are globally decentralized to serve as being strong enough to stop any type of hack or attack scenario. The KAPPI zone constitutes an individual blockchain which exchanges IBC messages to the DWARF.
The DWARF would conceive a zone to be a multiple asset membership dynamic with a multiple signature account capable of sending and receiving tokens through IBC packets. Like any cryptocurrency account, zones cannot transfer a token if they do not have that token to send but are able to receive tokens. Zones can use one or more types of tokens, which gives it the ability to inflate token supplies. Atoms of the KAPPI DWARF can be staked by any validator of a zone which is connected to the DWARF. This could result in a double spend attack, but it would be slashed through the KAPPI fork accountability, a zone where voting power cannot create any invalid state. KAPPI DWARF will not execute or verify any transaction that is committed in another DWARF, so users must send tokens to trustworthy zones.
Why Kappi?
Kappi solved many problems from the existing blockchain:
KAPPI is able to decipher the blockchain design through offering an easy API that functions between the consensus process and the application process. KAPPI consists of parallel blockchain networks which are all supported independently by classic BFT consensus algorithms such as KAPPI. The first blockchain in the network is KAPPI DWARF, which is connected to several zones or other blockchains through a unique inter-blockchain communication protocol. KAPPI DWARF can track many types of tokens and stores all tokens in each connected zone.
Tokens can be transferred from one zone to another quickly and safely without the need for physical fluid exchange between zones. This is possible due to the fact that all coin transfers are made between Zones will all go through KAPPI DWARF, which acts as a solution to many of the problems faced by the blockchain in contemporary times.
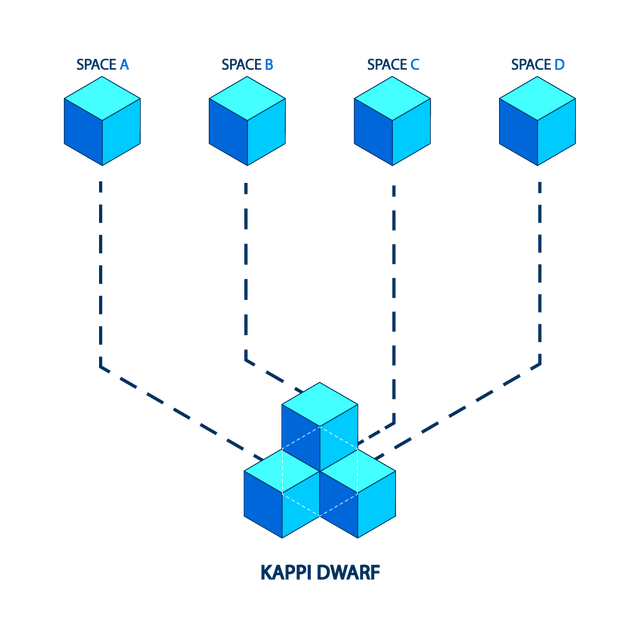
Some problems are solved using this architecture, including issues of scalability, interoperability, and flawless enhancements. Regardless of where the zone originates, including if it was created on Bitcoin, CryptoNote, Go-Ethereum or Cash, among others, it can be plugged into KAPPI DWARF. This allows unlimited scalability to the future and shows that this zone is perfect for operating distributed exchanges. KAPPI is not just a distributed ledger, but instead creates a protocol for each distributed exchange network. Transparency, a healthy economy, accountability theory and consensus are all included. KAPPI validators operate the same as miners in Bitcoin, except that it uses cryptographic signatures to vote.
KAPPI Consensus Protocol
The KAPPI consensus protocol and the interface which was used to build the application is backed by nodes which retain voting power which is no-negative. This is different than the classic Byzantine Fault Tolerant (BFT) algorithm that has each node carrying the same weight. In the KAPPI consensus, validators are able to participate in the consensus protocol through broadcasting cryptographic
based signatures, which are referred to as votes, that agree on the next block. The voting power of each validator is determined at genesis and can be altered deterministically within the blockchain, which would be dependent on what the application is. An example of this is that the staking tokens can be bonded as collateral to determine the voting power. Unless all the validators have an equal
weight, fractions would not be used to refer to the validator but only for the total voting power.
An analogy can be made with Bitcoin, which is known as a cryptocurrency blockchain that operates by having each node carrying a fully audited Unspent Transaction Output (UTXO) database. If someone wished to create that type of system on an ABCI foundation the KAPPI DWARF would have the responsibility to share transactions and blocks between each node. This would establish an
immutable or canonical order to the transactions in the blockchain.
The ABCI application would maintain the responsibility for:
Scalability and Decentralization
KAPPI is comprised of a network of many blockchains that being powered by KAPPI. KAPPI allows many blockchains to be running concurrently with each other whilst retaining interoperability.
At its DWARF, KAPPI DWARF manages multiple independent blockchain ‘zones’, that are also referred to by some as shards. With a constant stream of block commits coming from zones on the DWARF, it can keep up with each zone’s information and its current state.
In turn, the zones keep up with the DWARF, but not each other except through the DWARF. Information packets are sent from one zon to another through the DWARF through Merkle-proof posting showing that the information was both sent and received accurately.
Distribution Token

Roadmap
Meet Our Team

- Daniel JonssonFounding father

- Anna LanonenDevelopment of Project Leaders

- Miguela WebsterNetwork Architect

- Anna KetolaThe developer

- Saad SherThe developer

- David AttardGraphic designer
For more clear information please visit the link below:
Author : Apel malang
Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar